A group of esteemed scientists working with 'horizon scanners' have identified 15 environmental issues that will affect the way we carry out our conservation goals. The report, entitled Horizon scan of global conservation issues for 2011 used a method called horizon scanning - a tool for anticipating issues and accumulating knowledge. Horizon scanning is a search for initial trends, opportunities and constraints that affect the likelihood of achieving objectives - in this case, the likelihood of successfully conserving the Earth's biodiversity.
In researching this report, the authors aimed to ''identify emerging issues that could have substantial impacts on the conservation of biological diversity and... to encourage policy-relevant, practical research on those issues''.
The 15 environmental issues discussed in the report, judged to be the most novel and potentially significant are:
Environmental consequences of increasing milk consumption in Asia
The results of increasing milk production could include habitat loss, reduced water quality and greater emissions of methane and nitrous oxide - both greenhouse gases.
New greenhouse gases
Nitrogen trifluoride and sulfuryl fluoride concentrations have been rising for the past 30 years. Both these gases have a higher warming potential than carbon dioxide. Their use in industry has increased, as they are substitutes for other gases regulated under the Kyoto or Montreal Protocols
Productivity in polar oceans
New communities of organisms are establishing on the sea bed and in the water column where sea ice was once present. These communities store an estimated 3,500,000 tonnes of carbon per year. This substantially affect marine food chains, but the results are not yet known.
Biological impacts of perfluorinated compounds
Perfluorinated compounds are used in manufacturing and are coming under increasing attention from toxicologists. They are endocrine disruptors and have been detected in the tissues of fish and birds. An accumulation of perfluorooctanoic acid raises the risk of thyroid disease in humans, but little research has been done into these compounds.Expansion in mining for lithium used in rechargeable batteries
Demand for rechargeable batteries increasing, especially as electric cars are becoming more popular. Lithium is a key component in rechargeable batteries. Unexploited lithium reserves are mainly found in shallow lakes in the Andean deserts. These saline lakes are key habitats for many species, including the threatened Andean flamingo.
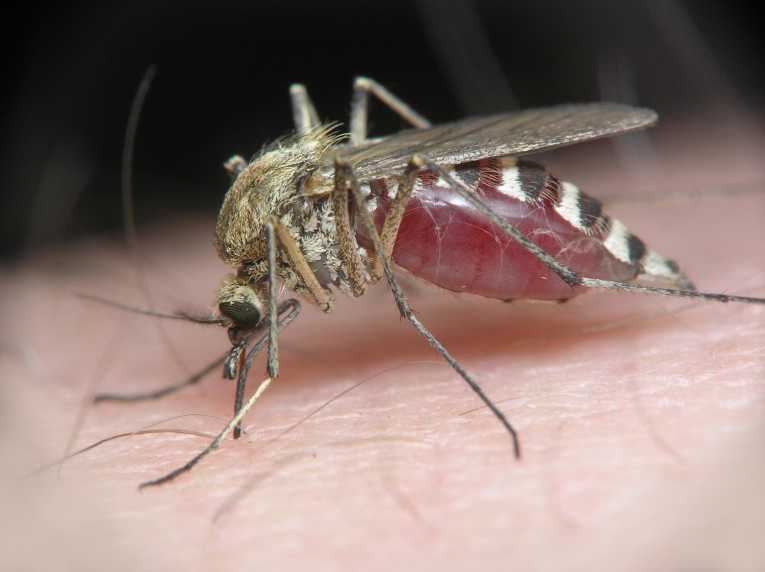
Genetic techniques to eradicate mosquitoes
Scientists eradicate several mosquito species and the diseases they carry, by modifying the mosquito genome. Although a truly great effort in the fight against human disease, the impact of such a project on biodiversity is unclear.
Nitric acid rain
Nitric acid rain is toxic to animals and can devastate fish populations. Species diversity is decreasing in grasslands across Europe, possibly due to the effect of acid rain.
Changes in soil ecology
An estimated 98 billion tonnes of carbon are emitted by soils each year, higher than previous estimates. If this is due to plant roots, the carbon release could be balanced by carbon dioxide absorption during photosynthesis. However, if the carbon release is due to microbes, it is likely that there will be a net release of carbon to the atmosphere. This may speed up the rate of climate change.
Denial of biodiversity loss
Researchers suggest that the percentage of people who deny the evidence for biodiversity loss will increase. This could have serious repercussions for climate, energy and biodiversity policies.
Protected area failure
Some areas set up to conserve specific habitats just aren't working, due to increasing agricultural pressure and human population growth.
Re-emergence of rinderpest
Although rinderpest in cattle has been eradicated due to a vaccination project, which has now stopped, it could yet re-emerge as a mutation from other, similar pathogens. This would have devastating effects on wild cattle populations and agriculture.
Climate governance
The Kyoto Protocol expires in 2012 and there is no agreement on what should replace it. The role of conservation in future agreements is unclear.
Transformation of oceans
Fish farming and marine energy projects are on the rise, along with other marine-based projects. Rapid, simultaneous developments in several countries will have a huge impact on marine species.
Earthworms in North American forests
European earthworms have colonised American forests - not as innocent as it sounds. Earthworms affect entire ecosystems - transforming the soils and affecting plant-herbivore interactions. Long term consequences of the transformation in North American forests are unclear.
Hydraulic fracturing
Carried out to extract gas from shale basins and a growth industry in the U.S. Hydraulic fracturing affects huge areas - 30% of Pennsylvania's forests have been made available - and water pollution is a real risk. Worryingly, hydraulic fracturing is exempt from the U.S. Safe Drinking Water Act and as such unregulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
For more information on these environmental issues, see Horizon scan of global conservation issues for 2011.